- SAP ABAP
- What is SAP ABAP
- SAP ABAP Data Dictionary and Domain
- SAP ABAP Data Element
- SAP ABAP Database Table
- SAP ABAP Database tables and views
- SAP ABAP Foreign Key
- SAP ABAP Indexes
- SAP ABAP Structure
- SAP ABAP Package
- SAP ABAP Adding Fields to SAP Standard Table
- SAP ABAP Internal Table and Database Table
- SAP ABAP Select Option and Parameter
- SAP ABAP Types of Internal Table
- SAP ABAP ways of Declaring Internal Tables
- SAP ABAP Mastering Initialization Technique
- SAP ABAP Operations on Internal Table
- SAP ABAP Record Retrieval
- SAP ABAP Insert, Modify and Delete data in the Internal table by using Keywords
- SAP ABAP Sorting and Removing Adjacent Duplicates
- SAP ABAP Seamless Data Transfer Between Internal Tables
- SAP ABAP Search Help Types
- SAP ABAP Lock Objects and Types
- SAP ABAP Buffering and Its Types
- SAP ABAP TMG
- SAP ABAP Table Types
- SAP ABAP Views
- SAP ABAP Control Break Statement
- SAP ABAP COMMIT and ROLLBACK
- SAP ABAP Joins
- SAP For All Entries
- SAP ABAP Procedure to Fill Final Internal Table
- SAP ABAP Modularization
- SAP ABAP Function Group and Function Module
- SAP ABAP SELECT Options
24DDIC1407 – What is Foreign Key and Technical Prerequisite to establish?
Foreign Keys in Database Management
A foreign key is a field in one table that establishes a link between the data in two tables. It ensures the data integrity of the foreign key table by validating the entries against a set of values in another table, known as the check table.
Technical Requirements for Establishing a Foreign Key Relationship
- Matching Domains: The fields in both tables must have the same data type and domain.
- Primary Key in Check Table: The referenced field in the check table must be a primary key.
Steps to Establish a Foreign Key Relationship
- Access SE11: Open the SE11 transaction in your system.
- Select Database Object: Choose the “Database Table” radio button.
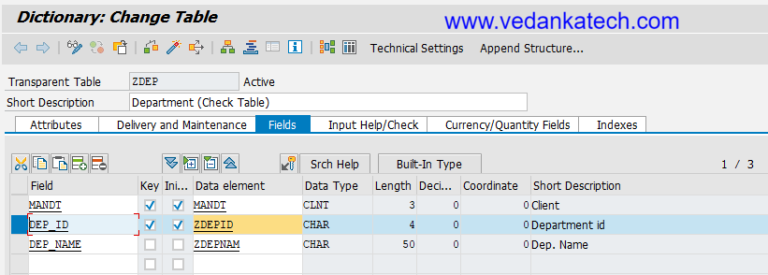
- Provide Foreign Key Table Name: Enter the name of the table where you want to establish the foreign key.
- Change Table Definition: Click on “Change” to modify the table definition.
- Select Fields: Highlight the fields for which you want to establish the foreign key relationship.
- Select Database Object: Choose the “Database Table” radio button.
- Provide Foreign Key Table Name: Enter the name of the table where you want to establish the foreign key.
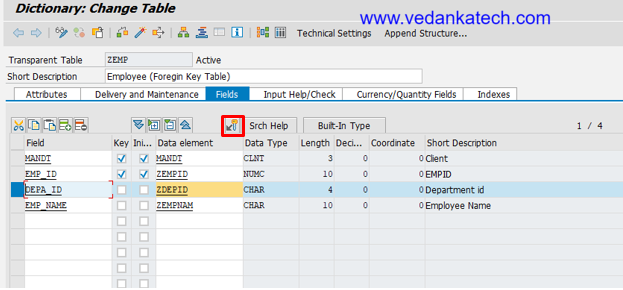
- Change Table Definition: Click on “Change” to modify the table definition.
- Select Fields: Highlight the fields for which you want to establish the foreign key relationship.
- Foreign Key Icon: Click on the foreign key icon under the fields tab.
Enter Check Table Name: Provide the short text, name of the check table that contains the primary key.
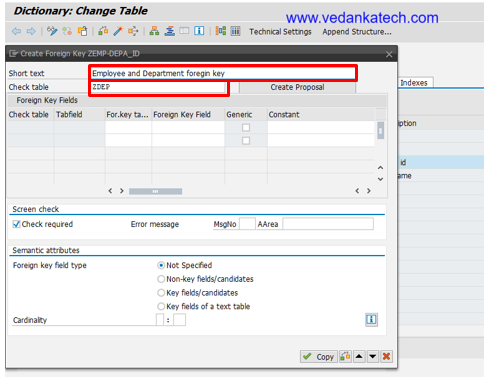
- Create Proposal: Click on “Create Proposal” The system will automatically propose the relationship between the tables.
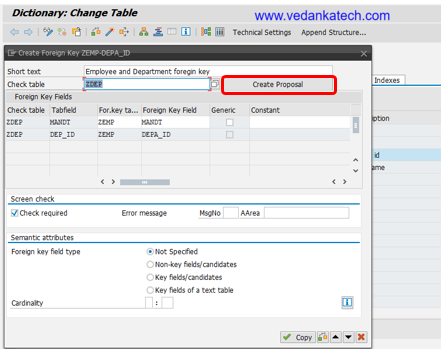
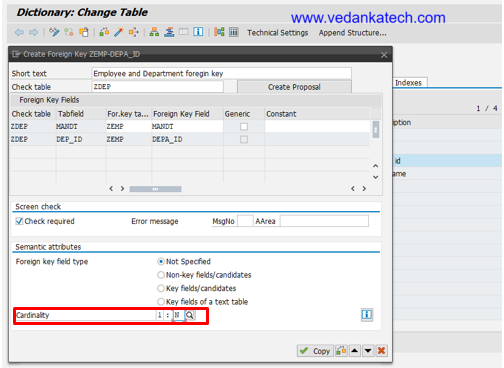
- Cardinality: Specify appropriate Cardinality by defining how many records in one table are related to records in another table for maintaining data integrity between the tables.
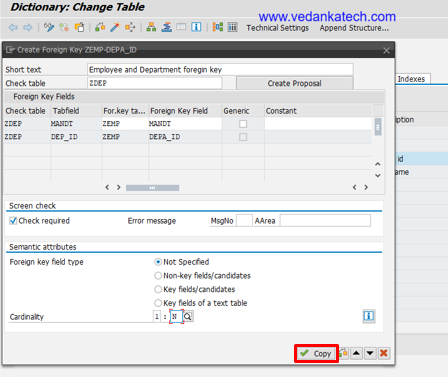
- Finalize: Press “Copy” then save, check and activate the table.
Following these steps will help you establish a robust foreign key relationship ensuring data integrity and consistency across your database.
Author : Aniket Pawar, 9373518385
24DDIC1407 – What is Foreign Key and Technical Prerequisite to establish?
Foreign Keys in Database Management
A foreign key is a field in one table that establishes a link between the data in two tables. It ensures the data integrity of the foreign key table by validating the entries against a set of values in another table, known as the check table.
Technical Requirements for Establishing a Foreign Key Relationship
- Matching Domains: The fields in both tables must have the same data type and domain.
- Primary Key in Check Table: The referenced field in the check table must be a primary key.
Steps to Establish a Foreign Key Relationship
- Access SE11: Open the SE11 transaction in your system.

- Select Database Object: Choose the “Database Table” radio button.
- Provide Foreign Key Table Name: Enter the name of the table where you want to establish the foreign key.
- Change Table Definition: Click on “Change” to modify the table definition.
- Select Fields: Highlight the fields for which you want to establish the foreign key relationship.

- Select Database Object: Choose the “Database Table” radio button.
- Provide Foreign Key Table Name: Enter the name of the table where you want to establish the foreign key.
- Change Table Definition: Click on “Change” to modify the table definition.
- Select Fields: Highlight the fields for which you want to establish the foreign key relationship.
- Foreign Key Icon: Click on the foreign key icon under the fields tab.

Enter Check Table Name: Provide the short text, name of the check table that contains the primary key.

- Create Proposal: Click on “Create Proposal” The system will automatically propose the relationship between the tables.

- Cardinality: Specify appropriate Cardinality by defining how many records in one table are related to records in another table for maintaining data integrity between the tables.

- Finalize: Press “Copy” then save, check and activate the table.

Following these steps will help you establish a robust foreign key relationship ensuring data integrity and consistency across your database.
Author : Aniket Pawar, 9373518385

