- SAP ABAP
- What is SAP ABAP
- SAP ABAP Data Dictionary and Domain
- SAP ABAP Data Element
- SAP ABAP Database Table
- SAP ABAP Database tables and views
- SAP ABAP Foreign Key
- SAP ABAP Indexes
- SAP ABAP Structure
- SAP ABAP Package
- SAP ABAP Adding Fields to SAP Standard Table
- SAP ABAP Internal Table and Database Table
- SAP ABAP Select Option and Parameter
- SAP ABAP Types of Internal Table
- SAP ABAP ways of Declaring Internal Tables
- SAP ABAP Mastering Initialization Technique
- SAP ABAP Operations on Internal Table
- SAP ABAP Record Retrieval
- SAP ABAP Insert, Modify and Delete data in the Internal table by using Keywords
- SAP ABAP Sorting and Removing Adjacent Duplicates
- SAP ABAP Seamless Data Transfer Between Internal Tables
- SAP ABAP Search Help Types
- SAP ABAP Lock Objects and Types
- SAP ABAP Buffering and Its Types
- SAP ABAP TMG
- SAP ABAP Table Types
- SAP ABAP Views
- SAP ABAP Control Break Statement
- SAP ABAP COMMIT and ROLLBACK
- SAP ABAP Joins
- SAP For All Entries
- SAP ABAP Procedure to Fill Final Internal Table
- SAP ABAP Modularization
- SAP ABAP Function Group and Function Module
- SAP ABAP SELECT Options
24DDIC1007 – Data Dictionary and Understanding SAP ABAP Domain Use and Steps to Create it
Data Dictionary
The SAP ABAP Data Dictionary (DDIC) is a centralized repository within the SAP system that defines and manages all the metadata and data structures, such as tables, views, data elements and domains, ensuring data consistency and integrity across the SAP environment.
Tcode
The transaction code (Tcode) to execute and access the SAP Data Dictionary is SE11.
SAP ABAP Domain
In SAP ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming) a domain defines the technical properties of a data element, such as data type, length and possible value range. It provides a central place to maintain and enforce data consistency across different tables and structures. By using domains, developers can ensure uniformity in the definition of data types, leading to better data integrity and easier maintenance.
Steps to Create an SAP ABAP Domain
- Access the ABAP Dictionary
Transaction Code: Enter transaction code SE11 in the SAP command field.
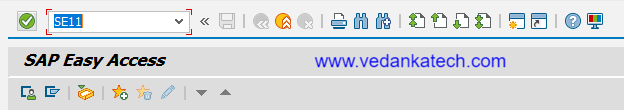
Select Domain: Choose the “Domain” option in the initial screen.

- Define the Domain Name
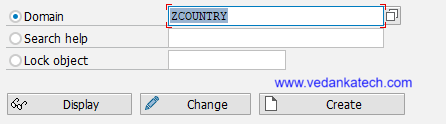
Naming Convention: Enter a unique domain name following the naming conventions of your organization and Click on Create.
Description: Provide a meaningful short description for the domain.
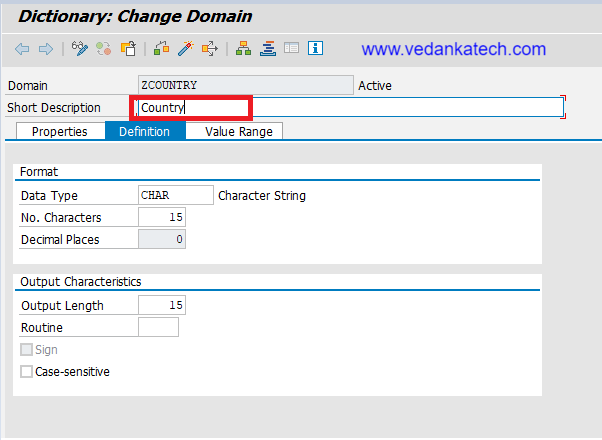
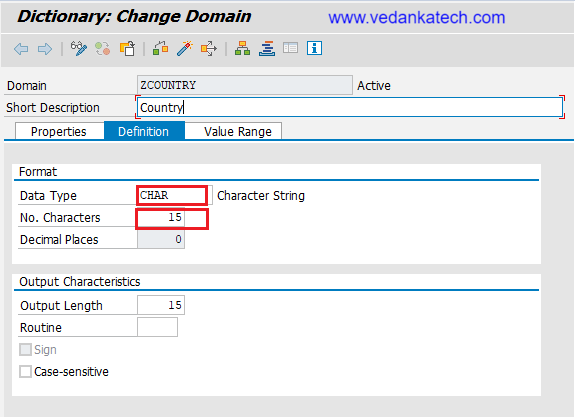
- Specify Data Type and Length
Data Type: Select the appropriate data type (e.g., CHAR, NUMC, DEC, etc.) for the domain.
Length: Define the length of the data type as required.
- Define Value Range
Fixed Values: Set fixed values or a range of acceptable values to ensure data integrity.
Value Table: Optionally, specify a value table that lists all permissible values.

- Set Output Characteristics
Conversion Routines: If needed, specify conversion routines for formatting and displaying the data.
Labels: Define field labels for different lengths (short, medium, long, and heading).
- Activate the Domain
Fixed Values: Set fixed values or a range of acceptable values to ensure data integrity.
Value Table: Optionally, specify a value table that lists all permissible values.
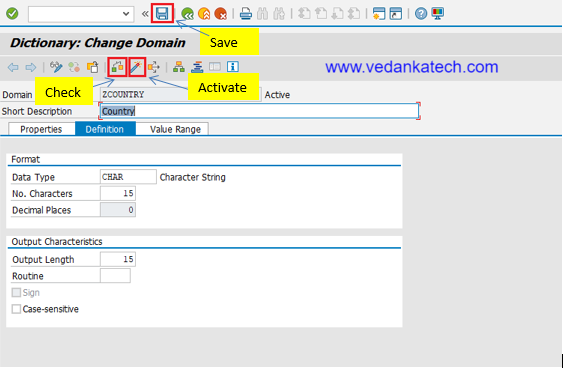
By following these steps, you can create a robust and reusable domain in SAP ABAP that helps in maintaining data consistency and integrity across your SAP system.
Author : Aniket Pawar, 9373518385
24DDIC1007 – Data Dictionary and Understanding SAP ABAP Domain Use and Steps to Create it
Data Dictionary
The SAP ABAP Data Dictionary (DDIC) is a centralized repository within the SAP system that defines and manages all the metadata and data structures, such as tables, views, data elements and domains, ensuring data consistency and integrity across the SAP environment.
Tcode
The transaction code (Tcode) to execute and access the SAP Data Dictionary is SE11.
SAP ABAP Domain
In SAP ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming) a domain defines the technical properties of a data element, such as data type, length and possible value range. It provides a central place to maintain and enforce data consistency across different tables and structures. By using domains, developers can ensure uniformity in the definition of data types, leading to better data integrity and easier maintenance.
Steps to Create an SAP ABAP Domain
- Access the ABAP Dictionary
Transaction Code: Enter transaction code SE11 in the SAP command field.

Select Domain: Choose the “Domain” option in the initial screen.

- Define the Domain Name

Naming Convention: Enter a unique domain name following the naming conventions of your organization and Click on Create.
Description: Provide a meaningful short description for the domain.

- Specify Data Type and Length
Data Type: Select the appropriate data type (e.g., CHAR, NUMC, DEC, etc.) for the domain.
Length: Define the length of the data type as required.

- Define Value Range
Fixed Values: Set fixed values or a range of acceptable values to ensure data integrity.
Value Table: Optionally, specify a value table that lists all permissible values.

- Set Output Characteristics
Conversion Routines: If needed, specify conversion routines for formatting and displaying the data.
Labels: Define field labels for different lengths (short, medium, long, and heading).
- Activate the Domain
Fixed Values: Set fixed values or a range of acceptable values to ensure data integrity.
Value Table: Optionally, specify a value table that lists all permissible values.

By following these steps, you can create a robust and reusable domain in SAP ABAP that helps in maintaining data consistency and integrity across your SAP system.
Author : Aniket Pawar, 9373518385

