- SAP ABAP
- What is SAP ABAP
- SAP ABAP Data Dictionary and Domain
- SAP ABAP Data Element
- SAP ABAP Database Table
- SAP ABAP Database tables and views
- SAP ABAP Foreign Key
- SAP ABAP Indexes
- SAP ABAP Structure
- SAP ABAP Package
- SAP ABAP Adding Fields to SAP Standard Table
- SAP ABAP Internal Table and Database Table
- SAP ABAP Select Option and Parameter
- SAP ABAP Types of Internal Table
- SAP ABAP ways of Declaring Internal Tables
- SAP ABAP Mastering Initialization Technique
- SAP ABAP Operations on Internal Table
- SAP ABAP Record Retrieval
- SAP ABAP Insert, Modify and Delete data in the Internal table by using Keywords
- SAP ABAP Sorting and Removing Adjacent Duplicates
- SAP ABAP Seamless Data Transfer Between Internal Tables
- SAP ABAP Search Help Types
- SAP ABAP Lock Objects and Types
- SAP ABAP Buffering and Its Types
- SAP ABAP TMG
- SAP ABAP Table Types
- SAP ABAP Views
- SAP ABAP Control Break Statement
- SAP ABAP COMMIT and ROLLBACK
- SAP ABAP Joins
- SAP For All Entries
- SAP ABAP Procedure to Fill Final Internal Table
- SAP ABAP Modularization
- SAP ABAP Function Group and Function Module
- SAP ABAP SELECT Options
24DDIC1507 – Enhancing Query Performance with Indexes and Steps to create Secondary Index
Indexes are essential for improving the performance of select queries in a database. There are two main types of indexes:
- Primary Index
- Secondary Index
Primary Index
A primary index is based on the primary fields of a table. It’s crucial for the structure of the database as a table cannot exist without a primary index. You can define up to 16 primary indexes per table. However, primary indexes can only be created for custom tables, not for standard tables.
Secondary Index
Secondary indexes are created on fields other than the primary ones. Unlike primary indexes, a table can exist without a secondary index. You can define up to 9 secondary indexes per table and they can be created for both standard and custom tables.
Note:
Domains assigned to data elements cannot be deleted.
Data elements assigned to database tables cannot be deleted.
You can create database tables without data elements using the direct method or predefined types.
Creating and Managing Secondary Indexes in SAP ABAP: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Access SE11 Transaction Code
Execute the tcode “SE11” in the SAP command field to open the ABAP Dictionary.
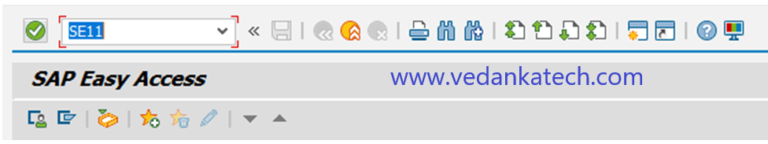
Step 2: Open the Database Table
In the ABAP Dictionary: Initial screen, enter the database table name you wish to modify and click the “Change” button.
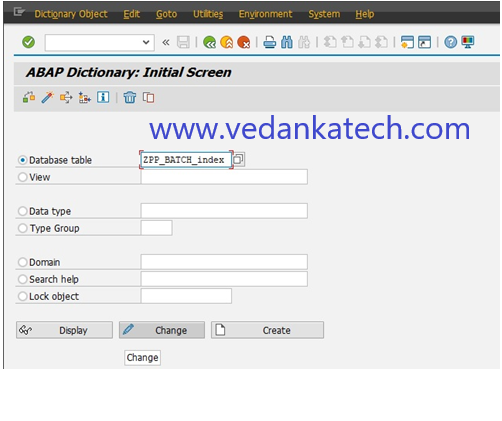
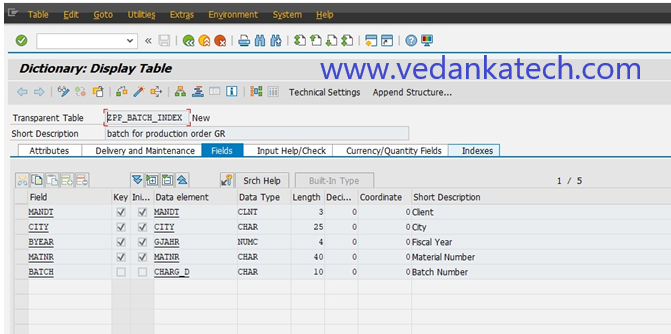
Step 3: Access Indexes
On the Dictionary maintenance screen, click on the “Indexes” Tab.
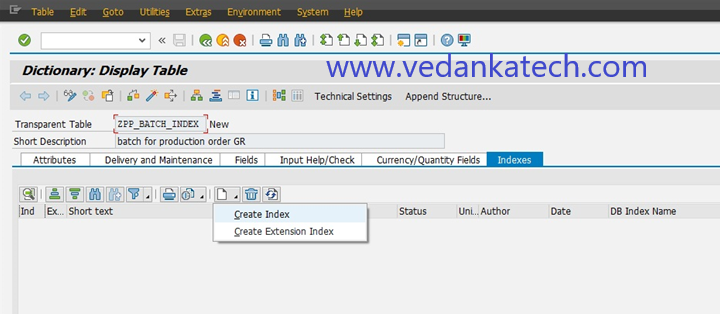
Step 4: Create a New Index
click the “Create” icon. Select “Create Index” from the options.
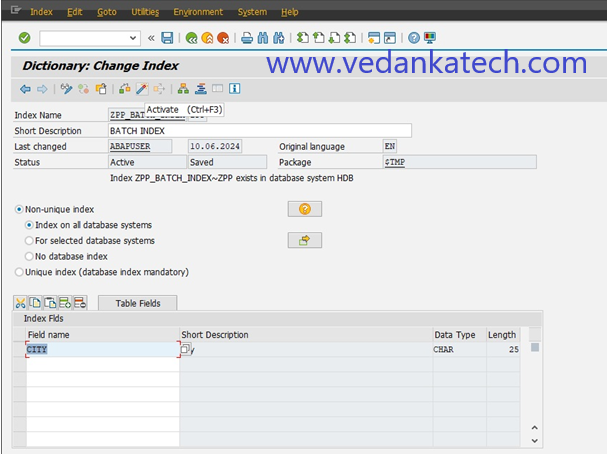
Step 5: Name the Index
Enter a name for the index, which can be up to 3 characters long and press Enter to proceed.
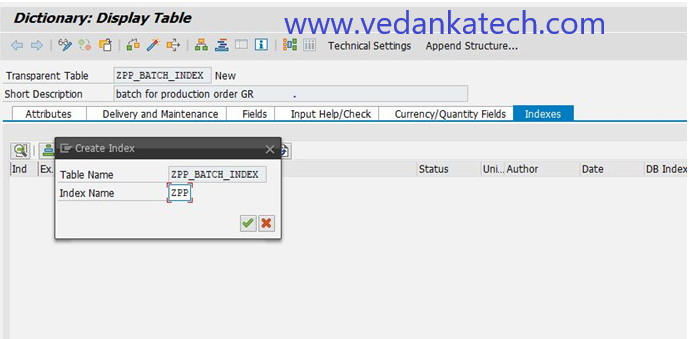
Step 6: Define Index Details
On the “Dictionary: Maintain Index” screen, provide the following details:
Short Description: Enter a brief description of the secondary index.
Table Fields: Select the fields that will be included in the index.
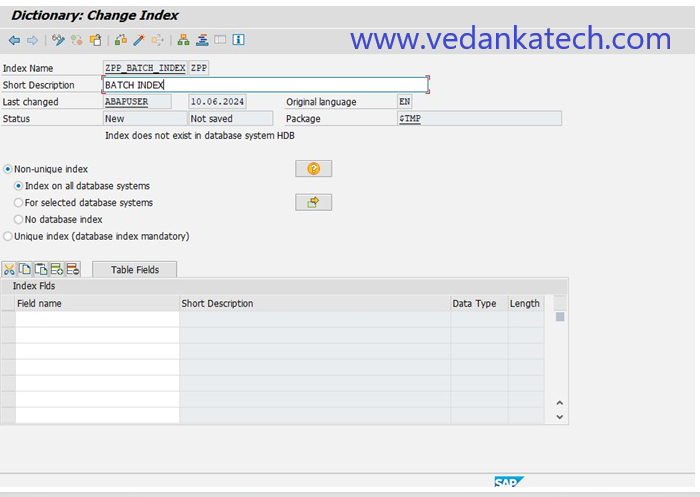
Step 7: Select Fields
Choose the necessary fields and click the “Copy” button to include them in the index.
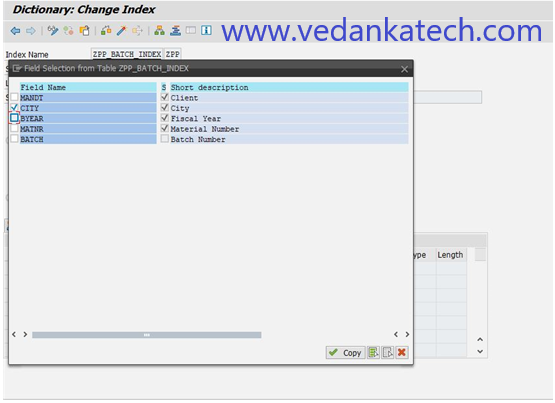
Step 8: Save the Index
Choose the local object to save the created SAP ABAP indexes.
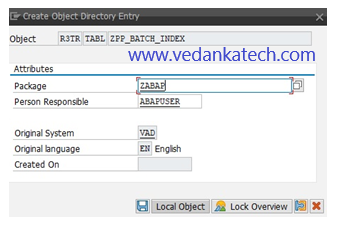
Step 9: Activate the Index
Click on the “Activate” icon to finalize and activate the newly created index.
Deleting Secondary Indexes in SAP ABAP
Step 1: Access SE11 Transaction Code
Refer to steps 1 through 3 from the creation process to navigate to the indexes option for the desired table.
Step 2: Select the Index to Delete
Choose the index you want to delete and click the “Delete” icon.
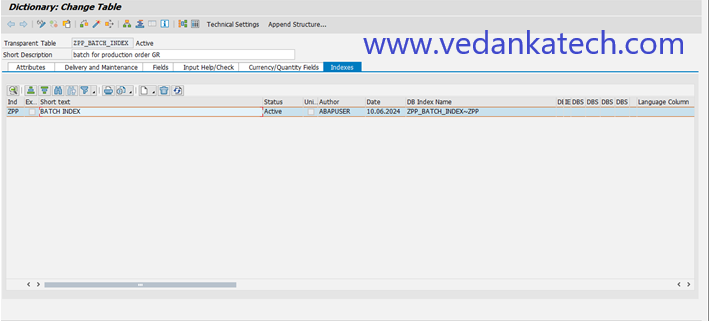
Step 3: Confirm Deletion
A warning message will appear select “Yes” to confirm and delete the index.
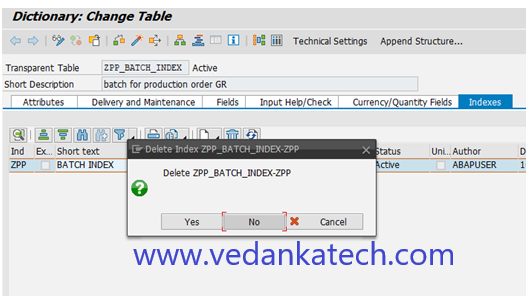
By following these steps, you can efficiently create and manage secondary indexes in SAP ABAP, optimizing your database performance and data retrieval processes.
Author : Aniket Pawar, 9373518385
24DDIC1507 – Enhancing Query Performance with Indexes and Steps to create Secondary Index
Indexes are essential for improving the performance of select queries in a database. There are two main types of indexes:
- Primary Index
- Secondary Index
Primary Index
A primary index is based on the primary fields of a table. It’s crucial for the structure of the database as a table cannot exist without a primary index. You can define up to 16 primary indexes per table. However, primary indexes can only be created for custom tables, not for standard tables.
Secondary Index
Secondary indexes are created on fields other than the primary ones. Unlike primary indexes, a table can exist without a secondary index. You can define up to 9 secondary indexes per table and they can be created for both standard and custom tables.
Note:
Domains assigned to data elements cannot be deleted.
Data elements assigned to database tables cannot be deleted.
You can create database tables without data elements using the direct method or predefined types.
Creating and Managing Secondary Indexes in SAP ABAP: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Access SE11 Transaction Code
Execute the tcode “SE11” in the SAP command field to open the ABAP Dictionary.

Step 2: Open the Database Table
In the ABAP Dictionary: Initial screen, enter the database table name you wish to modify and click the “Change” button.

Step 3: Access Indexes
On the Dictionary maintenance screen, click on the “Indexes” Tab.

Step 4: Create a New Index
click the “Create” icon. Select “Create Index” from the options.

Step 5: Name the Index
Enter a name for the index, which can be up to 3 characters long and press Enter to proceed.

Step 6: Define Index Details
On the “Dictionary: Maintain Index” screen, provide the following details:
Short Description: Enter a brief description of the secondary index.
Table Fields: Select the fields that will be included in the index.

Step 7: Select Fields
Choose the necessary fields and click the “Copy” button to include them in the index.

Step 8: Save the Index
Choose the local object to save the created SAP ABAP indexes.

Step 9: Activate the Index
Click on the “Activate” icon to finalize and activate the newly created index.

Deleting Secondary Indexes in SAP ABAP
Step 1: Access SE11 Transaction Code
Refer to steps 1 through 3 from the creation process to navigate to the indexes option for the desired table.
Step 2: Select the Index to Delete
Choose the index you want to delete and click the “Delete” icon.

Step 3: Confirm Deletion
A warning message will appear select “Yes” to confirm and delete the index.

By following these steps, you can efficiently create and manage secondary indexes in SAP ABAP, optimizing your database performance and data retrieval processes.
Author : Aniket Pawar, 9373518385

